- Clone
- 37.51 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Tp44, T44
- Isotype
- Syrian Hamster IgG
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
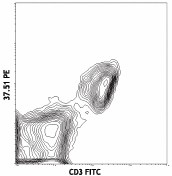
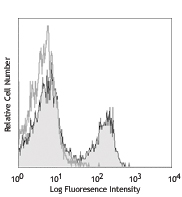
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 37.51 PE and CD3 FITC
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 102101 | 50 µg | 44€ | ||||
| 102102 | 500 µg | 102€ | ||||
CD28 is a 44 kD glycoprotein, also known as Tp44 or T44. It is a member of the Ig superfamily, expressed on thymocytes, most peripheral T cells, and NK cells. In association with CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2), CD28 acts as the second signal for T and NK cell activation and proliferation. The 37.51 antibody has been reported to augment in vitro T cell proliferation and cytokine production, and promote CTL development.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Syrian Hamster
- Immunogen
- C57BL/6 mouse T-cell lymphoma EL-4
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The CD28 antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
IP, IHC-F, Costim, Block - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
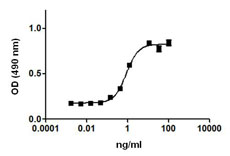
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation1, in vitro costimulation of T and NK cells1, in vitro blocking of allogeneic mixed leukocyte response and inhibition of MHC-unrestricted CTL cytotoxicity3,4, in vitro induction of thymocyte differentiation2,5-9,11, and immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections. For in vivo studies or highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) (Cat. No. 102116).
- Application References
-
- Gross JA, et al. 1992. J. Immunol. 149:380. (IP, Costim)
- Cibotti R, et al. 1997. Immunity 6:245. (Costim)
- Masten BJ, et al. 1997. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 16:335. (Block)
- Nishio M, et al. 1996. J. Immunol. 157:4347. (Block)
- Zhang N and He Y-W, 2005. J. Exp. Med. 202:395. (Costim)
- Terrazas LI, et al. 2005. Intl. J. Parasitology. 35:1349. (Costim)
- Perchonock CE, et al. 2006. Mol Cell Biol. 26(16):6005. (Costim)
- Wang W, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:4885. (Costim)
- Pua HH, et al. 2007. J. Exp. Med. 204:25. (Costim)
- Perchonock CE, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:1768.
- Barbi J, et al. 2007. Blood 110:2215.
- Milpied P, et al. 2011. Blood 118:2993. PubMed
- Cunningham NR, et al. 2011. Int Immunol. 23:693. PubMed
- Crispin JC, et al. 2012. J. Immunol. 188:3567. PubMed
- Li CR, et al. 2014. J Immunol. 192:1425. PubMed
- Blankenhaus B, et al. 2014. PLoS Pathog. 10:1003913. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_312866 (BioLegend Cat. No. 102101)
AB_312867 (BioLegend Cat. No. 102102)
- Disclaimer
-
This product may be used for research purposes only. It is not licensed for resale and may only be used by the buyer. This product may not be used and is not licensed for clinical assays where the results of such assays are provided as a diagnostic service. If a diagnostic or therapeutic use is anticipated then a license must be requested from the University of California. The availability of such diagnostic and therapeutic use license(s) cannot be guaranteed from the University of California.
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, 44 kD
- Distribution
-
Thymocytes, CD4+, CD8+ peripheral T cells, NK cells
- Function
- Costimulates T and NK cells
- Ligand/Receptor
- CD80 (B7-1), CD86 (B7-2)
- Cell Type
- NK cells, T cells, Thymocytes, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay AN, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Lenschow DJ, et al. 1996. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:233.
3. Gross JA, et al. 1992. J. Immunol. 149:380. - Gene ID
- 12487 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD28 on UniProt.org
Other Formats
View All CD28 Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| APC anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| Biotin anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| PE anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| Purified anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC,IP,IHC-F,Costim,Block |
| PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC,IP,IHC-F,Costim,Block |
| Purified anti-mouse CD28 (Maxpar® Ready) | 37.51 | FC,CyTOF® |
| PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| TotalSeq™-C0204 anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | PG |
| KIRAVIA Blue 520™ anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | FC |
| TotalSeq™-A0204 anti-mouse CD28 | 37.51 | PG |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse CD28

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 FITC and CD2... 
-
Biotin anti-mouse CD28

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 APC and Biot... 
-
PE anti-mouse CD28
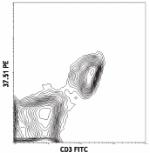
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 37.51 PE and CD3 FITC -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD28

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD3ε ... -
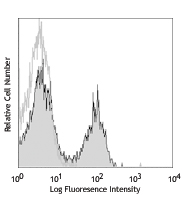
Purified anti-mouse CD28

C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with 37.51 PE and CD3 FITC -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD28
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 APC and CD28... -
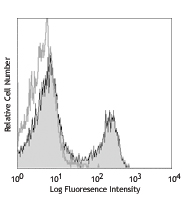
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD28
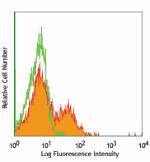
C57BL/6 splenocytes stained with LEAF™ purified 37.51, follo... -
Purified anti-mouse CD28 (Maxpar® Ready)

BALB/c mouse splenocytes stained with 151Eu-anti-CD28 (37.51... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD28
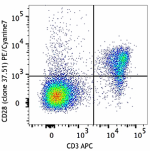
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 APC and CD28... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD28
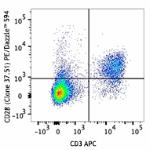
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 (clone 145-2... 
-
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD28

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 PE and CD28 ... 
-
TotalSeq™-C0204 anti-mouse CD28
-
KIRAVIA Blue 520™ anti-mouse CD28
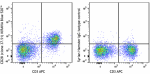
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3 APC and anti... -
TotalSeq™-A0204 anti-mouse CD28
 Login / Register
Login / Register 








Follow Us