 Clone A17035K recognizes beta-secretase, also known as beta-site APP cleavage enzyme 1 (BACE1), a protease expressed in neurons. The cleavage of APP at the N-terminus of the Aβ domain by BACE1 releases a soluble extracellular fragment called sAPPβ. The remaining portion of APP, which is membrane-bound, is termed C-terminal fragment (C99).
Clone A17035K recognizes beta-secretase, also known as beta-site APP cleavage enzyme 1 (BACE1), a protease expressed in neurons. The cleavage of APP at the N-terminus of the Aβ domain by BACE1 releases a soluble extracellular fragment called sAPPβ. The remaining portion of APP, which is membrane-bound, is termed C-terminal fragment (C99).
 Though not catalytically active itself, Nicastrin is a critical component of gamma-secretase, and is responsible for promoting maturation and localization of other units to the enzymatic complex. Clone 9C3 can detect Nicastrin by western blotting and IHC.
Though not catalytically active itself, Nicastrin is a critical component of gamma-secretase, and is responsible for promoting maturation and localization of other units to the enzymatic complex. Clone 9C3 can detect Nicastrin by western blotting and IHC.
 Clone NT1 can be used to detect presenilin 1, another component of gamma-secretase. Gamma-secretase is responsible for the processing of the C99 fragment to release Aβ isoforms, including Aβ 1-40 and Aβ 1-42, and a fragment known as the APP intracellular domain (AICD). Increased Aβ production has been partly attributed to mutations in the APP or PSEN genes. These mutations favor the processing of APP by β- and γ-secretases leading to elevated levels of Aβ.
Clone NT1 can be used to detect presenilin 1, another component of gamma-secretase. Gamma-secretase is responsible for the processing of the C99 fragment to release Aβ isoforms, including Aβ 1-40 and Aβ 1-42, and a fragment known as the APP intracellular domain (AICD). Increased Aβ production has been partly attributed to mutations in the APP or PSEN genes. These mutations favor the processing of APP by β- and γ-secretases leading to elevated levels of Aβ.
 Clone PS2 can be used to detect presenilin 2, which is also a component of gamma-secretase, by western blotting. Mutations in presenilin 1 and 2 are major causative factors of early onset familial Alzheimer’s disease.
Clone PS2 can be used to detect presenilin 2, which is also a component of gamma-secretase, by western blotting. Mutations in presenilin 1 and 2 are major causative factors of early onset familial Alzheimer’s disease.
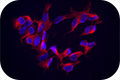 Clone TUJ1 is highly reactive to class III β-tubulin, a cytoskeletal protein expressed in neurons. Clone TUJ1 does not react with β-tubulin found in glial cells. Immunostaining with TUJ1 allows visualization of cell bodies, dendrites, and axons.
Clone TUJ1 is highly reactive to class III β-tubulin, a cytoskeletal protein expressed in neurons. Clone TUJ1 does not react with β-tubulin found in glial cells. Immunostaining with TUJ1 allows visualization of cell bodies, dendrites, and axons.
 Login/Register
Login/Register 



 Clone A17035K recognizes beta-secretase, also known as beta-site APP cleavage enzyme 1 (BACE1), a protease expressed in neurons. The cleavage of APP at the N-terminus of the Aβ domain by BACE1 releases a soluble extracellular fragment called sAPPβ. The remaining portion of APP, which is membrane-bound, is termed C-terminal fragment (C99).
Clone A17035K recognizes beta-secretase, also known as beta-site APP cleavage enzyme 1 (BACE1), a protease expressed in neurons. The cleavage of APP at the N-terminus of the Aβ domain by BACE1 releases a soluble extracellular fragment called sAPPβ. The remaining portion of APP, which is membrane-bound, is termed C-terminal fragment (C99). Though not catalytically active itself, Nicastrin is a critical component of gamma-secretase, and is responsible for promoting maturation and localization of other units to the enzymatic complex. Clone 9C3 can detect Nicastrin by western blotting and IHC.
Though not catalytically active itself, Nicastrin is a critical component of gamma-secretase, and is responsible for promoting maturation and localization of other units to the enzymatic complex. Clone 9C3 can detect Nicastrin by western blotting and IHC. Clone NT1 can be used to detect presenilin 1, another component of gamma-secretase. Gamma-secretase is responsible for the processing of the C99 fragment to release Aβ isoforms, including Aβ 1-40 and Aβ 1-42, and a fragment known as the APP intracellular domain (AICD). Increased Aβ production has been partly attributed to mutations in the APP or PSEN genes. These mutations favor the processing of APP by β- and γ-secretases leading to elevated levels of Aβ.
Clone NT1 can be used to detect presenilin 1, another component of gamma-secretase. Gamma-secretase is responsible for the processing of the C99 fragment to release Aβ isoforms, including Aβ 1-40 and Aβ 1-42, and a fragment known as the APP intracellular domain (AICD). Increased Aβ production has been partly attributed to mutations in the APP or PSEN genes. These mutations favor the processing of APP by β- and γ-secretases leading to elevated levels of Aβ. Clone PS2 can be used to detect presenilin 2, which is also a component of gamma-secretase, by western blotting. Mutations in presenilin 1 and 2 are major causative factors of early onset familial Alzheimer’s disease.
Clone PS2 can be used to detect presenilin 2, which is also a component of gamma-secretase, by western blotting. Mutations in presenilin 1 and 2 are major causative factors of early onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Clone TUJ1 is highly reactive to class III β-tubulin, a cytoskeletal protein expressed in neurons. Clone TUJ1 does not react with β-tubulin found in glial cells. Immunostaining with TUJ1 allows visualization of cell bodies, dendrites, and axons.
Clone TUJ1 is highly reactive to class III β-tubulin, a cytoskeletal protein expressed in neurons. Clone TUJ1 does not react with β-tubulin found in glial cells. Immunostaining with TUJ1 allows visualization of cell bodies, dendrites, and axons.


Follow Us