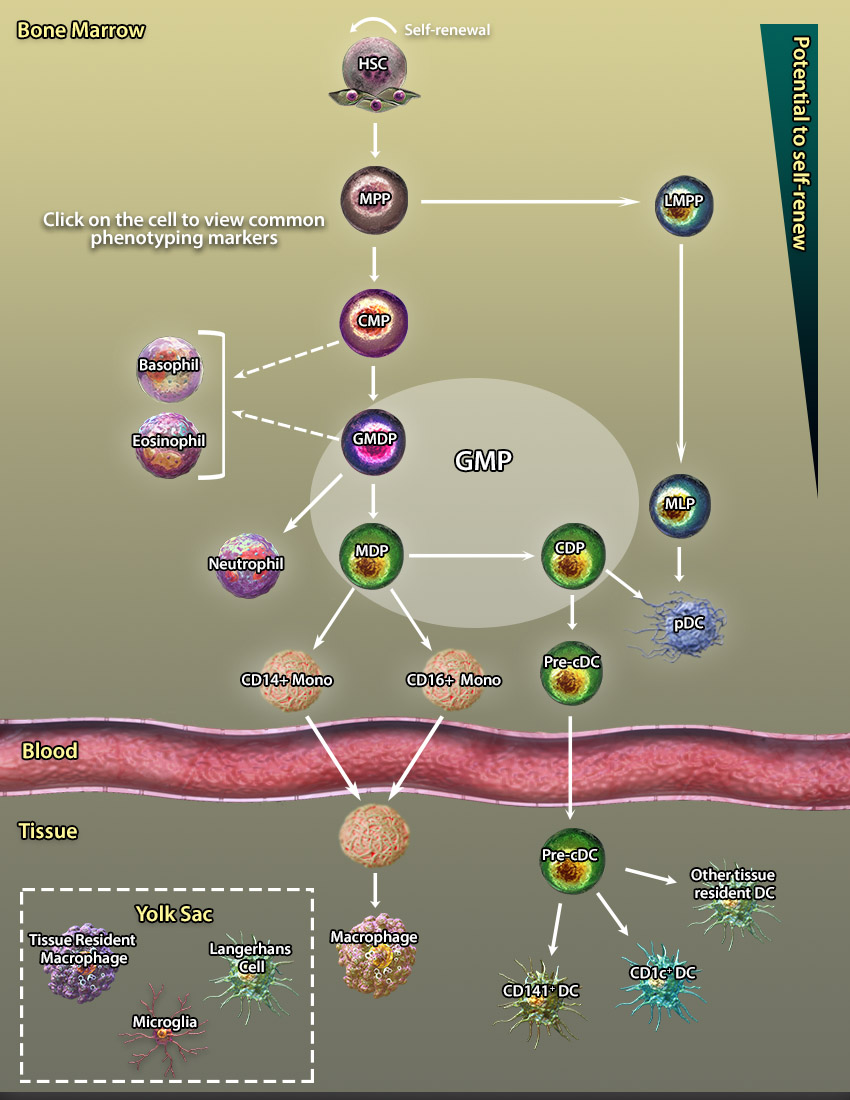
Myelopoiesis defines the development of non-lymphoid leukocytes from the hematopoietic stem cells. This process can be further sub-divided into granulopoiesis, which generates basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils, and monocytopoiesis, which creates monocytes that can develop into macrophages and dendritic cells.
Explore our interactive graphics below by clicking on each cell type to bring up a list of markers expressed at that stage of development.
Select a species to begin:
|
|
|
 Login / Register
Login / Register 



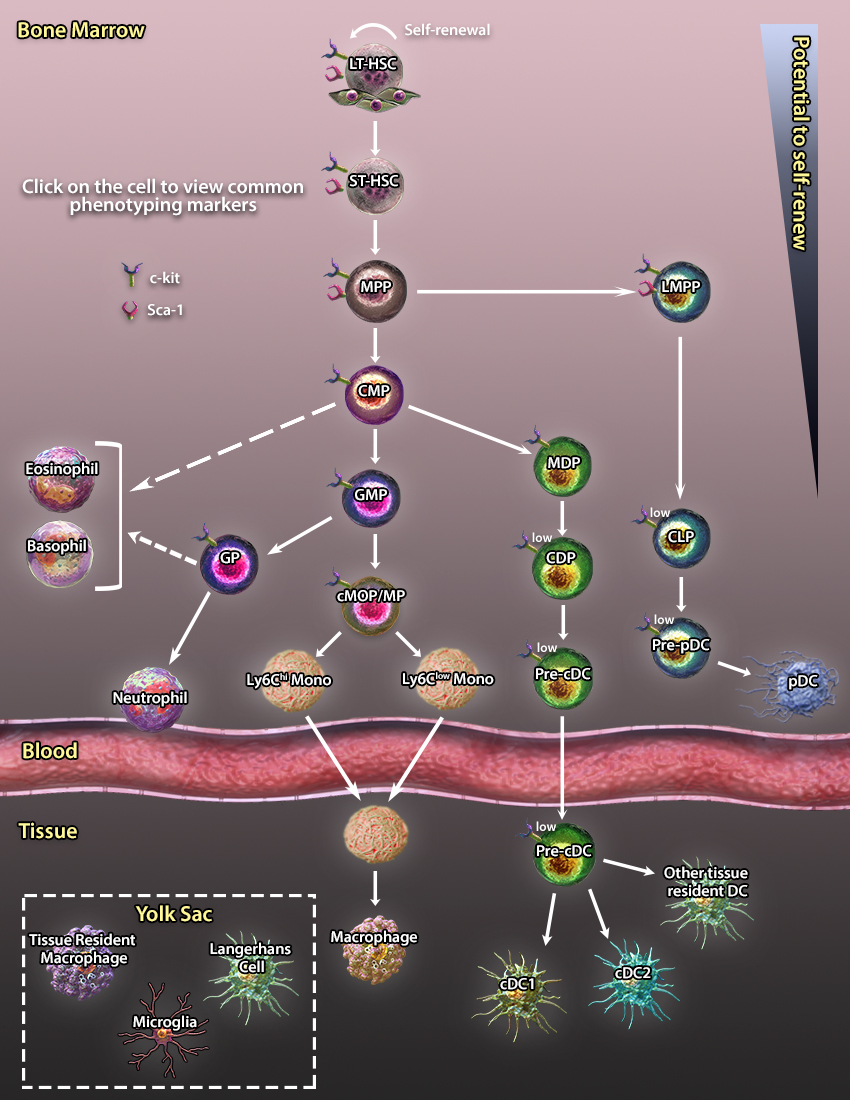
 LT-HSCs are pluripotent cells which give rise to all blood cell populations of lymphoid, myeloid, and erythroid lineages and persist throughout the entire life-span. They have the potential to self-renew sustaining the stem cell pool or differentiate into ST-HSCs and other multi-, oligo-, and unipotent progenitors which give rise to terminally differentiated cells.
LT-HSCs are pluripotent cells which give rise to all blood cell populations of lymphoid, myeloid, and erythroid lineages and persist throughout the entire life-span. They have the potential to self-renew sustaining the stem cell pool or differentiate into ST-HSCs and other multi-, oligo-, and unipotent progenitors which give rise to terminally differentiated cells. MPPs are multipotent progenitors derived from ST-HSCs. They can give rise to another multipotent progenitor, LMPPs, or oligopotent and unipotent progenitors which give rise to terminally differentiated cells.
MPPs are multipotent progenitors derived from ST-HSCs. They can give rise to another multipotent progenitor, LMPPs, or oligopotent and unipotent progenitors which give rise to terminally differentiated cells. LMPPs are responsible for the generation of lymphocytes and pDCs through subsequent differentiation steps including CLPs and pre-pDCs respectively. LMPPs were originally thought to be a homogeneous population of precursors containing multipotent cells with the equal potential to differentiate into several lymphoid lineages. However, a recent study has demonstrated that LMPP is a heterogeneous population of cells comprising unipotent clones with a non-overlapping lineage differentiation potential (21).
LMPPs are responsible for the generation of lymphocytes and pDCs through subsequent differentiation steps including CLPs and pre-pDCs respectively. LMPPs were originally thought to be a homogeneous population of precursors containing multipotent cells with the equal potential to differentiate into several lymphoid lineages. However, a recent study has demonstrated that LMPP is a heterogeneous population of cells comprising unipotent clones with a non-overlapping lineage differentiation potential (21). CMPs are oligopotent progenitor derived from MPPs. This progenitor can differentiate into erythroid and myeloid lineages. It was originally believed that CMPs were a homogeneous population of precursor cells containing multipotent cells with the equal potential to differentiate into both myeloid and lymphoid lineages. However, a recent study has demonstrated that instead CMPs are a heterogeneous population of cells comprised of unipotent clones with a non-overlapping potential to give rise to an erythroid or myeloid lineage of cells (11,12).
CMPs are oligopotent progenitor derived from MPPs. This progenitor can differentiate into erythroid and myeloid lineages. It was originally believed that CMPs were a homogeneous population of precursor cells containing multipotent cells with the equal potential to differentiate into both myeloid and lymphoid lineages. However, a recent study has demonstrated that instead CMPs are a heterogeneous population of cells comprised of unipotent clones with a non-overlapping potential to give rise to an erythroid or myeloid lineage of cells (11,12). GMPs are oligopotent progenitor derived from CMPs. This progenitor gives rise to monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils), and some tissue dendritic cells through differentiation steps including GPs and cMOPs. A recent study suggests that GMPs are a heterogeneous population of cells comprised of unipotent clones with a nonoverlapping potential to give rise to monocytes, macrophages, and granulocytes (11). In order to separate GMPs (
GMPs are oligopotent progenitor derived from CMPs. This progenitor gives rise to monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils), and some tissue dendritic cells through differentiation steps including GPs and cMOPs. A recent study suggests that GMPs are a heterogeneous population of cells comprised of unipotent clones with a nonoverlapping potential to give rise to monocytes, macrophages, and granulocytes (11). In order to separate GMPs ( cMOP/MPs are oligopotent progenitor cells derived from GMPs and MDPs. cMOP/MPs differentiate to Ly-6Chi and Ly-6Clow monocytes which can differentiate further into macrophages and dendritic cells.
cMOP/MPs are oligopotent progenitor cells derived from GMPs and MDPs. cMOP/MPs differentiate to Ly-6Chi and Ly-6Clow monocytes which can differentiate further into macrophages and dendritic cells. MDPs are oligopotent progenitors which give rise to monocytes and dendritic cell populations (cDC1, cDC2, pDC). The relationship between MDPs and other progenitor populations is not fully understood.
MDPs are oligopotent progenitors which give rise to monocytes and dendritic cell populations (cDC1, cDC2, pDC). The relationship between MDPs and other progenitor populations is not fully understood. pDCs are derived from Pre-pDC s in the bone marrow. pDCs play key role in antiviral responses and produce IFN type I cytokines.
pDCs are derived from Pre-pDC s in the bone marrow. pDCs play key role in antiviral responses and produce IFN type I cytokines. cDC1s, also known as CD8α+ DCs, are derived from Pre-cDCs in the bone marrow. cDC1s one of the key antigen presenting cells responsible for cross-presenting antigens to CD8+ T cells and priming of Th1 and Treg cells.
cDC1s, also known as CD8α+ DCs, are derived from Pre-cDCs in the bone marrow. cDC1s one of the key antigen presenting cells responsible for cross-presenting antigens to CD8+ T cells and priming of Th1 and Treg cells. cDC2s, also known as
cDC2s, also known as  Tissue-resident dendritic cells are derived from Pre-cDCs during steady-state or from monocytes during inflammation in the tissue. Tissue-resident cells are subcategorized into
Tissue-resident dendritic cells are derived from Pre-cDCs during steady-state or from monocytes during inflammation in the tissue. Tissue-resident cells are subcategorized into  Macrophages are a part of the mononuclear phagocytic system. They play a critical role in inflammatory responses involving bacterial infections and tissue injuries. Originally, tissue-resident macrophages are derived from the embryonic precursor in the yolk sac. In adulthood, the peripheral pool of macrophages is maintained by monocytes.
Macrophages are a part of the mononuclear phagocytic system. They play a critical role in inflammatory responses involving bacterial infections and tissue injuries. Originally, tissue-resident macrophages are derived from the embryonic precursor in the yolk sac. In adulthood, the peripheral pool of macrophages is maintained by monocytes. Basophils belong to a subclass of granulocytes differentiated in the bone marrow from the GMP precursor. Basophils circulate in the blood and control allergy responses by performing different functions, including production of histamine and regulation of IgE levels via secretion of IL-4 cytokine.
Basophils belong to a subclass of granulocytes differentiated in the bone marrow from the GMP precursor. Basophils circulate in the blood and control allergy responses by performing different functions, including production of histamine and regulation of IgE levels via secretion of IL-4 cytokine. Eosinophils belong to a subclass of granulocytes differentiated in the bone marrow from the GMP precursor. eosinophils have been shown to play an essential role in parasite infections (i.e. helminth infection) and some allergic reactions including asthma. eosinophils are potent mediators of T helper responses by production of Th1 (i.e., IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, IL-25) and Th2 (IL-12, IFN-γ) cytokines.
Eosinophils belong to a subclass of granulocytes differentiated in the bone marrow from the GMP precursor. eosinophils have been shown to play an essential role in parasite infections (i.e. helminth infection) and some allergic reactions including asthma. eosinophils are potent mediators of T helper responses by production of Th1 (i.e., IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13, IL-25) and Th2 (IL-12, IFN-γ) cytokines. Neutrophils are the most abundant leukocytes circulating in the blood. The lifespan of neutrophils is very short. The daily replenishment of the neutrophil peripheral pool happens via differentiation of neutrophils from GPs in the bone marrow. neutrophils patrol blood vessels, scavenging for pathogen-derived antigens and are one of the primary innate immune subsets to be recruited to sites of inflammation where they produce a plethora of antimicrobial peptides and proteins including α-defensins, lysozymes, and lactoferrin.
Neutrophils are the most abundant leukocytes circulating in the blood. The lifespan of neutrophils is very short. The daily replenishment of the neutrophil peripheral pool happens via differentiation of neutrophils from GPs in the bone marrow. neutrophils patrol blood vessels, scavenging for pathogen-derived antigens and are one of the primary innate immune subsets to be recruited to sites of inflammation where they produce a plethora of antimicrobial peptides and proteins including α-defensins, lysozymes, and lactoferrin. LCs are members of dendritic cell family and serve as antigen presenting cells in the skin. Unlike other dendritic cell types, LCs are derived from progenitors residing in the yolk sac during embryogenesis. In adulthood, the peripheral pool of LCs can be replenished by monocytes.
LCs are members of dendritic cell family and serve as antigen presenting cells in the skin. Unlike other dendritic cell types, LCs are derived from progenitors residing in the yolk sac during embryogenesis. In adulthood, the peripheral pool of LCs can be replenished by monocytes. Microglia are specialized antigen presenting cells identified in brain parenchyma. Microglia cells are derived from erythromyeloid progenitors in the yolk sac during primitive hematopoiesis around embryonic day 7.5-8 (E7.5-8). At steady-state, microglia cells are responsible for the removal of dead neurons and Aβ peptides, secretion of trophic factors such as BDNF, and synapse pruning. Under inflammatory signals, microglial cells become activated and differentiate into effective APCs.
Microglia are specialized antigen presenting cells identified in brain parenchyma. Microglia cells are derived from erythromyeloid progenitors in the yolk sac during primitive hematopoiesis around embryonic day 7.5-8 (E7.5-8). At steady-state, microglia cells are responsible for the removal of dead neurons and Aβ peptides, secretion of trophic factors such as BDNF, and synapse pruning. Under inflammatory signals, microglial cells become activated and differentiate into effective APCs. Monocyte development includes several precursor cells including GMPs, MDPs, and cMOPs. Upon inflammatory stimuli, Ly6Chi monocytes migrate into inflamed tissues where they secrete pro-inflammatory mediators (i.e., TNF-α, iNOS, IL-12, type 1 interferons) and give rise to inflammatory M1 macrophages and dendritic cells.
Monocyte development includes several precursor cells including GMPs, MDPs, and cMOPs. Upon inflammatory stimuli, Ly6Chi monocytes migrate into inflamed tissues where they secrete pro-inflammatory mediators (i.e., TNF-α, iNOS, IL-12, type 1 interferons) and give rise to inflammatory M1 macrophages and dendritic cells. GMPs are oligopotent progenitors derived from CMPs. Recent studies have shown that GMPs are a heterogeneous population of cells containing oligopotent progenitors such as GMDPs, MDPs, and CDPs. GMDPs differentiate to all myeloid lineages including mono/macs, granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils), and dendritic cells, while MDPs and CDPs give rise to monocytes and dendritic cells or only dendritic cells, respectively (5).
GMPs are oligopotent progenitors derived from CMPs. Recent studies have shown that GMPs are a heterogeneous population of cells containing oligopotent progenitors such as GMDPs, MDPs, and CDPs. GMDPs differentiate to all myeloid lineages including mono/macs, granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils), and dendritic cells, while MDPs and CDPs give rise to monocytes and dendritic cells or only dendritic cells, respectively (5).


Follow Us