Apotracker™ Tetra
Similar to Apotracker Green, Apotracker Tetra detects phosphatidylserine accumulation on dead and apoptotic cells without the use of cation-containing specialized buffers. The reagent contains two components: biotinylated monomeric peptides and fluorophore-conjugated streptavidin. Upon mixture of the two components and formation of a tetramer complex, the peptides undergo conformational changes, resulting in higher affinity binding of the peptide components to phosphatidylserine residues. This enables specific detection of dead and apoptotic cells, as well as extracellular vesicles.
Apotracker Tetra is currently available as a product bundle that includes the biotinylated monomer peptide and streptavidin-Alexa Fluor® 647, which is pre-diluted and titrated for ease of use. The biotinylated monomer components can then be paired with any available streptavidin-fluorophore option, providing additional flexibility in multicolor panel construction. For guidance on titration of your streptavidin conjugate, you can contact Technical Services.
Apotracker™ Tetra staining correlates with other apoptotic cell indicators
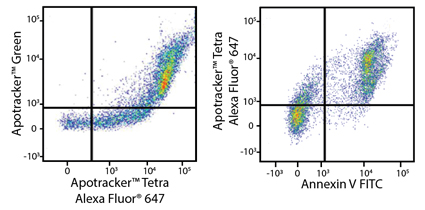 |
Heat-induced C57BL/6 splenocytes, containing 40% dead cells (left) and 50% dead cells (right) stained with Apotracker Green and Apotracker Tetra Alexa Fluor® 647. Signal of Apotracker Green and Apotracker Tetra Alexa Fluor® 647 showed a positive correlation (left). |
Apotracker™ Tetra stains both mouse splenocytes and human PBMCs
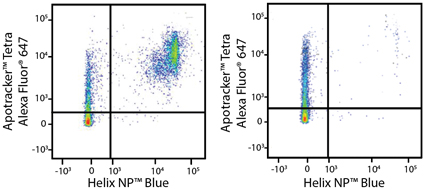 |
Heat-induced 50% dead C57BL/6 splenocytes (left) or untreated splenocytes (right) stained with Helix NP Blue and Apotracker Tetra Alexa Fluor® 647. |
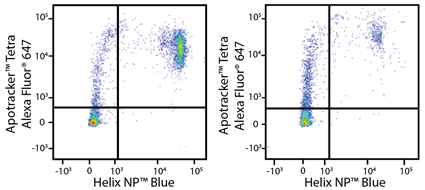 |
Heat-induced 50% dead PBMC (left) or untreated PBMC (right) stained with Helix NP Blue and Apotracker Tetra Alexa Fluor® 647. |






Follow Us