- Clone
- 1A8 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus G
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2a, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
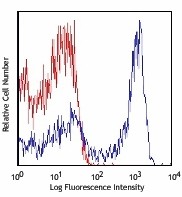
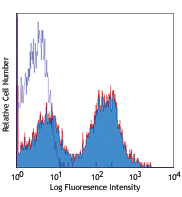
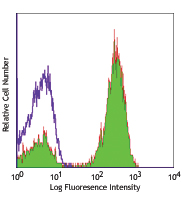
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 APC/Cyanine7
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 127623 | 25 µg | 80€ | ||||
| 127624 | 100 µg | 243€ | ||||
Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus G (Ly-6G), a 21-25 kD GPI-anchored protein, is expressed on the majority of myeloid cells in bone marrow and peripheral granulocytes.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Ly-6G transfected EL-4J cell line.
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with APC/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.25 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
While 1A8 recognizes only Ly-6G, clone RB6-8C5 recognizes both Ly-6G and Ly-6C. Clone RB6-8C5 binds with high affinity to mouse Ly-6G molecules and to a lower extent to Ly-6C15. Clone RB6-8C5 impairs the binding of anti-mouse Ly-6G clone 1A815. However, clone RB6-8C5 is able to stain in the presence of anti-mouse Ly-6C clone HK1.416.
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunohistochemistry9 of frozen sections10 and paraffin-embedded sections11, depletion4, 12-14, and spatial biology (IBEX)20,21. The Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for in vivo studies or highly sensitive assays (Cat. No. 127632, 127649, 127650, 127661 and 127662). - Additional Product Notes
- BioLegend is in the process of converting the name APC/Cy7 to APC/Cyanine7. The dye molecule remains the same, so you should expect the same quality and performance from our APC/Cyanine7 products. Please contact Technical Service if you have any questions.
- Application References
-
- Fleming TJ, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 151:2399. (FC)
- Daley JM, et al. 2008. J. Leukocyte Biol. 83:1. (FC)
- Dietlin TA, et al. 2007. J. Leukocyte Biol. 81:1205. (FC)
- Daley J, et al. 2007. J. Leukocyte Biol. doi:10.1189. (Deplete) PubMed
- Tadagavadi RK, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 185:4904. PubMed
- Sumagin R, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 185:7057. PubMed
- Guiducci C, et al. 2010. J. Exp Med. 207:2931. PubMed
- Fujita M, et al. 2011. Cancer Res. 71:2664. PubMed
- Van Leeuwen, et al. 2008. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28:84. (IHC)
- Kowanetz M, et al. 2010. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107:21248. [supplementary data] (IHC)
- Esbona K, et al. 2016. Breast Cancer Res. 18:35. (IHC)
- Wojtasiak M, et al. 2010. J. Gen. Virol. 91:2158. (FC, Deplete)
- Jaeger BN, et al. 2012. J. Exp. Med. 209:565. (Deplete)
- Wozniak KL, et al. 2012. BMC Immunol. 13:65 (FC, Deplete)
- Ribechini E, et al. 2009. Eur. J. Immunol. 39:3538.
- Ng LG, et al. 2011. J Invest. Dermatol. 131:2058. PubMed
- Ma C, et al. 2012. J. Leukoc. Biol. 92:1199.
- McCartney-Francis, N, et al. 2014. J Leukoc. Biol. 96:917. PubMed
- Her Z, et al. 2014. EMBO Mol. Med. 7:24. PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_10645331 (BioLegend Cat. No. 127623)
AB_10640819 (BioLegend Cat. No. 127624)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- A 21-35 kD GPI-anchorded membrane protein
- Distribution
-
Expressed on the majority of myeloid cells in bone marrow and peripheral granulocytes. The monoclonal antibody RB6-8C5 recognizes both Ly-6G and Ly-6C.
- Cell Type
- Granulocytes, Macrophages, Monocytes
- Biology Area
- Immunology, Innate Immunity
- Antigen References
-
Fleming TJ, et al. 1993. J. Immunol. 151:2399.
- Gene ID
- 546644 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Ly-6G on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All Ly-6G Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse Ly-6G
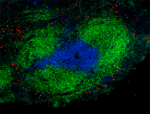
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
Purified anti-mouse Ly-6G
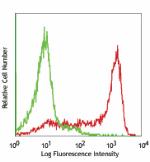
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 purified, followe... 
Fresh, frozen mouse spleen was stained with purified Ly6G cl... 
Mouse uterine tissue fixed in 10% formalin, paraffin embedde... -
Biotin anti-mouse Ly-6G
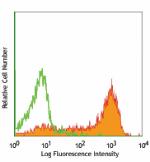
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 biotin, followed ... -
FITC anti-mouse Ly-6G
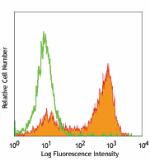
BALB/cmouse bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 FITC (gated o... -
PE anti-mouse Ly-6G
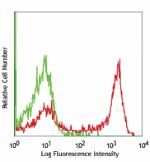
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 PE (gated on myel... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse Ly-6G
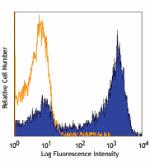
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 Alexa Fluor... 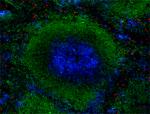
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
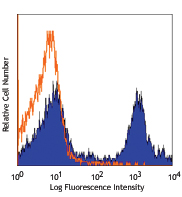
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse Ly-6G
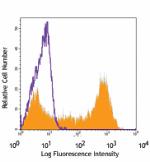
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 Pacific Blue&trad... -
APC anti-mouse Ly-6G
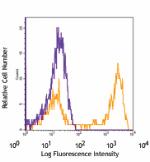
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 APC -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse Ly-6G
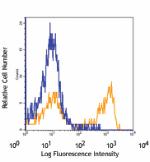
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 PerCP/Cyanine5.5 -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ly-6G
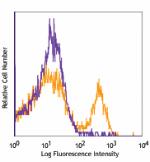
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 PE/Cyanine7 -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse Ly-6G
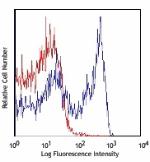
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 Alexa Fluor® ... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse Ly-6G
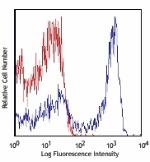
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 APC/Cyanine7 -
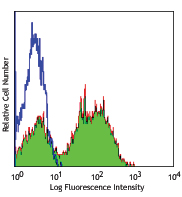
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse Ly-6G
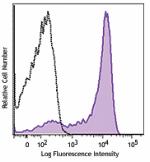
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... 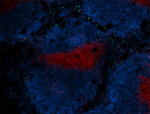
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 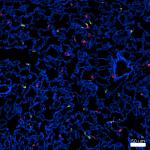
Confocal image of C57BL/6 mouse lung sample acquired using t... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse Ly-6G
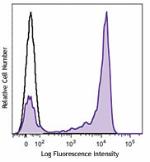
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... 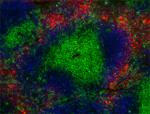
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse Ly-6G
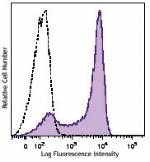
C57BL/6 bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clone 1A8... -
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse Ly-6G

C57BL/6 bone marrow cells stained with 1A8 purified, followe... 
Mouse uterine tissue fixed in 10% formalin, paraffin embedde... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse Ly-6G
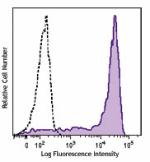
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
Purified anti-mouse Ly-6G (Maxpar® Ready)

C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with 148Nd-anti-CD11... 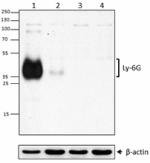
Western blot analysis of mouse bone marrow (lane 1), mouse s... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse Ly-6G
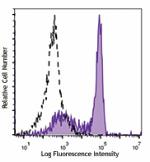
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse Ly-6G
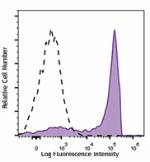
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse Ly-6G
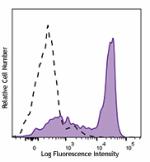
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse Ly-6G
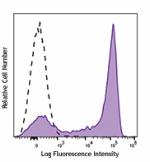
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse Ly-6G
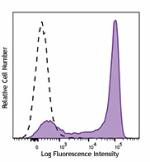
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse Ly-6G
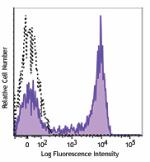
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
PerCP anti-mouse Ly-6G
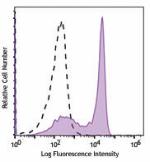
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
TotalSeq™-A0015 anti-mouse Ly-6G
-
TotalSeq™-C0015 anti-mouse Ly-6G
-
TotalSeq™-B0015 anti-mouse Ly-6G
-
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse Ly-6G
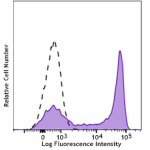
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with Ly-6G (clone 1A... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse Ly-6G
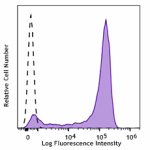
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with Ly-6G (clo... -
Spark YG™ 593 anti-mouse Ly-6G
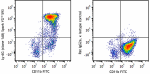
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
APC/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse Ly-6G Antibody
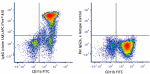
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse Ly-6G
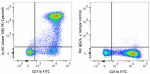
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
PE/Fire™ 810 anti-mouse Ly-6G Antibody
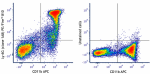
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse Ly-6G
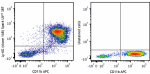
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... -
PE/Fire™ 640 anti-mouse Ly-6G
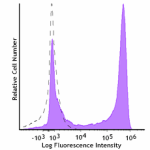
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with anti-mouse Ly-6... -
Spark YG™ 570 anti-mouse Ly-6G
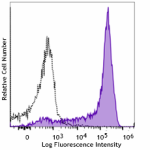
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells were stained with anti-mouse... 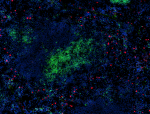
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 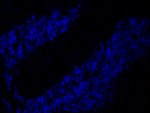
C57BL/6 mouse frozen cerebellum section was fixed with 4% pa...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 











Follow Us