- Clone
- Poly6221 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Actin, cytoplasmic 1
- Isotype
- Rabbit Polyclonal IgG
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
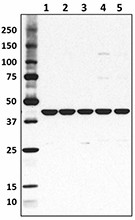
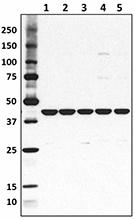
Total cell lysate from HeLa cells (lane 1, 15 µg), NIN3T3 cells (lane 2, 15 µg), U87-MG cells (lane 3, 15 µg), mouse brain (lane 4, 15 µg) and rat brain (lane 5, 15 µg) were resolved by electrophoresis (4-20% Tris-Glycine gel), transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with purified anti-β-actin antibody (Poly6221). Proteins were visualized using an HRP Donkey anti-rabbit IgG Antibody and chemiluminescence detection. -
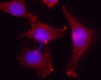
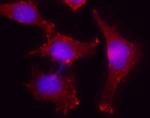
Immunofluorescent microscope analysis of Hela cells using Poly6221, followed by Rhodamine Red-X goat anti-rabbit IgG and DAPI. -
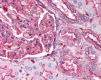
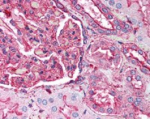
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human kidney tissue was stained with Poly6221 and developed with an alkaline phosphatase chromogen substrate (red color). Tissue was counterstained with H&E (blue/pink). Magnification, 40X.
β-actin is a ubiquitously expressed and highly conserved 42 kD cytoplasmic protein involved in cell motility. This critical cytoskeletal component can be disrupted by drugs such as cytochalasin. Because β-actin is ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells, it is frequently used as a loading control for assays involving protein detection (such as Western blotting). The Poly6221 antibody has been shown to be useful for Western blotting of mouse, rat, and human β-actin.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse, Rat, Human
- Antibody Type
- Polyclonal
- Host Species
- Rabbit
- Immunogen
- Peptide-KLH, NH2 terminus
- Formulation
- This antibody is provided in phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- Upon receipt, store frozen at -20°C.
- Application
-
WB - Quality tested
ICC, IHC-P - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by Western blotting. Western blotting, suggested working dilution(s): Use 10 µL per 5 mL antibody dilution buffer for each mini-gel. For immunocytochemistry: Use a dilution range of 1:100~1:400. For immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections, use a 1:100 dilution of antibody for staining. Antigen retrieval for IHC using 0.01 M sodium citrate buffer is recommended. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
This product may contain other non-IgG subtypes.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Lawson BR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:5366.
- Joyce CW. 2006. J. Biol. Chem. 281:33053.
- Yanagiya T,et al.2007.Obesity.15:572.PubMed
- KishidaT,et al.2007.J. Immunol. 179:8554.PubMed
- Ouimet M, et al. 2008. Arterisocler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1144. PubMed
- Toltlt LJ,et al. 2008.J. Immunol. 181:2165. PubMed
- Sawada. T,et al. 2008. J. Biol. Chem. 283:26820. PubMed
- Ikeda D, et al. 2008. Endocrinology. 149:6037. PubMed
- Rahman MK, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 184:7247. PubMed
- Shikama Y, et al. 2011. Innate Immun. 17:3. PubMed
- Zhang Y, et al. 2012. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:70. PubMed
- Piao X, et al. 2012. Sci Signal. 5:93. PubMed
- Ng CS, et al. 2013. J. Virol. 87:9511. PubMed
- Harvey BS, et al. 2014. Cytokine. 65:236. PubMed
- Diessner J, et al. 2014. Cell Death Dis. 5:1149. PubMed
- Hua X, et al. 2015. PloS One. 10:128039. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_315945 (BioLegend Cat. No. 622101)
AB_315946 (BioLegend Cat. No. 622102)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Member of the actin family; 42 KD
- Distribution
-
Ubiquitously expressed in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells
- Function
- Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility
- Interaction
- Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) that forms a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to four others.
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Cell Motility/Cytoskeleton/Structure, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- Microfilaments
- Antigen References
-
1. Hanukoglu I, et al. 1983. J. Mol. Biol. 163:673.
2. Nakajima-Iijima S, et al. 1985. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 82:6133.
3. Ponte P, et al. 1984. Nucleic Acids Res. 12:1687. - Regulation
- Three actin isoforms exist in vertebrates; alpha, found in muscle tissues; beta and gamma, found as cytoskeletal components and mediators of internal cell motility. Drugs such as cytochalasin disrupt the actin network.
- Gene ID
- 11461 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about beta-actin on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Related FAQs
Other Formats
View All β-Actin Reagents Request Custom Conjugation| Description | Clone | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Purified anti-β-actin | Poly6221 | WB,ICC,IHC-P |
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 








Follow Us