Neuroinflammation
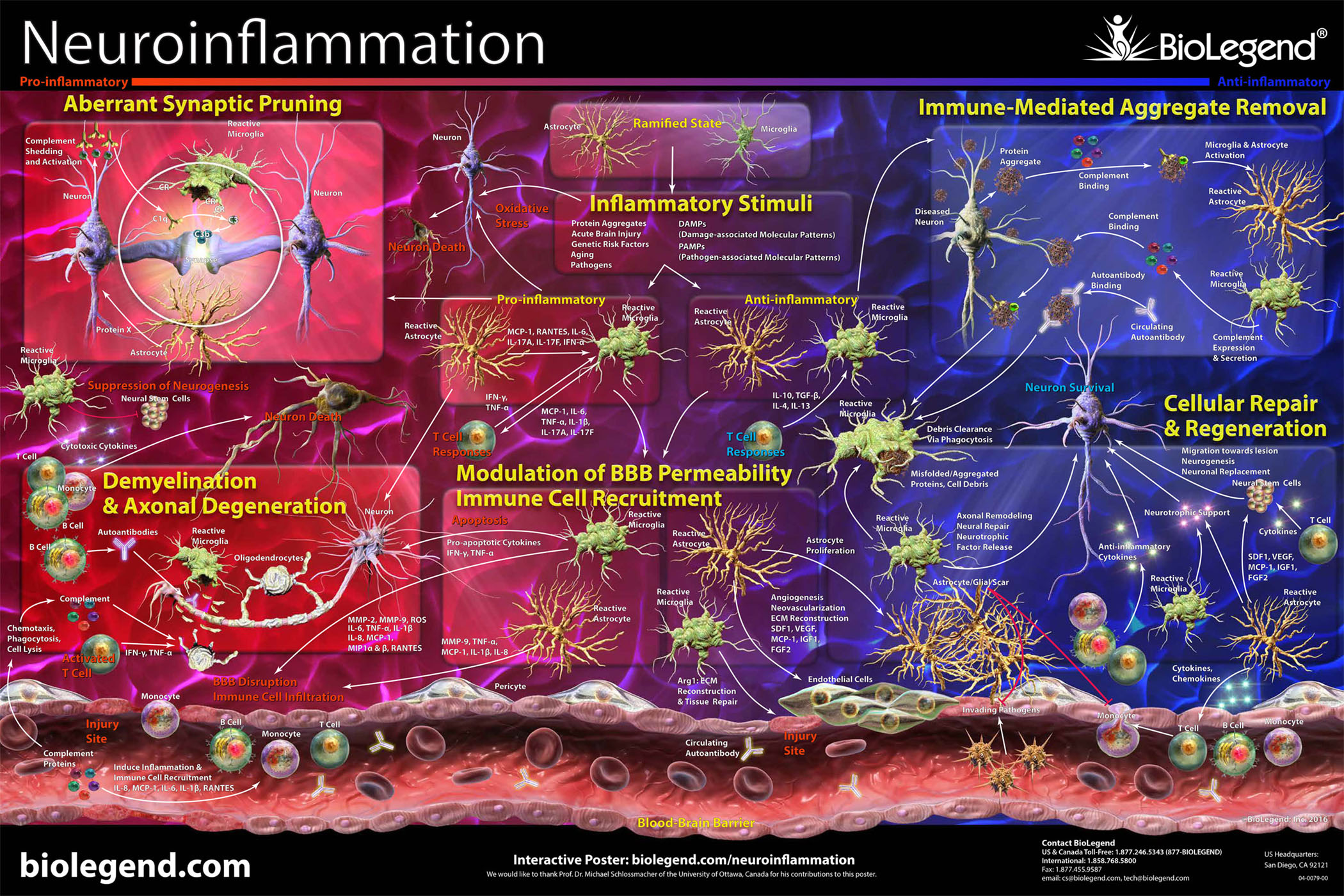
Neuroinflammation refers to the inflammation of the nervous tissue, and is an immune response often initiated against a variety of harmful stimuli such as pathogens or trauma. Neuroinflammation is a complex biological response involving many signaling proteins, receptors, and cell types. A combination of responses from resident glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS), which include microglia, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes, and non-glial resident myeloid cells including macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs), as well as peripheral leukocytes, constitute the basis for neuroinflammation in the CNS. Neuroinflammation plays an important role in many disorders of the nervous system and is a common component of many neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Production of toxic protein aggregates and/or metabolites in these disorders is often associated with chronic inflammation and sustained activation of resident brain immune cells. This response ultimately leads to the production of inflammatory molecules, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, recruitment of peripheral immune cells, and amplification of the immune response. Ultimately, chronic inflammation culminates in a variety of responses such as aberrant synaptic pruning, axonal demyelination and degeneration, and eventual loss of neurons.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us