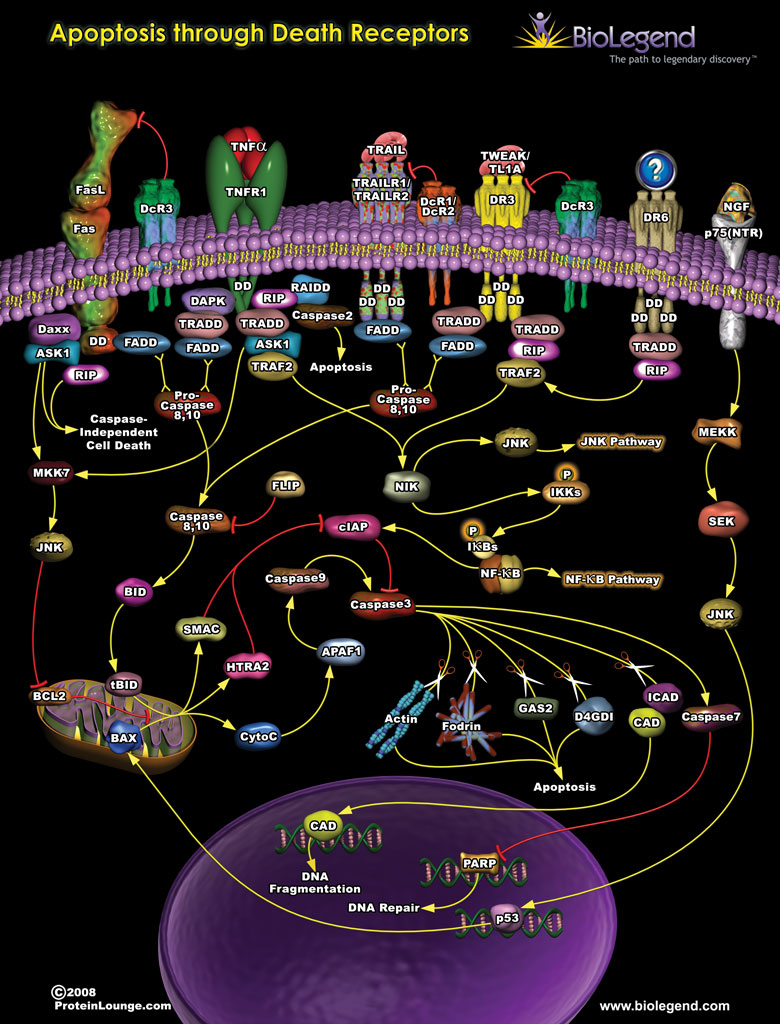
Apoptosis Through Death Receptors
Death receptors are members of the TNF superfamily, including FAS, TNFR1, and TRAIL1, which contain a specific cytoplasmic domain known as a death domain or DD. The death domains of these receptors primarily function to initiate signaling through pro-apoptotic pathways leading to cell death but can also have other functions in oncogenesis and inflammation. Initiation of these signaling cascades begins with the binding of ligands (FasL, TNF-α, TRAIL, TWEAK) to their respective receptors. Once the ligand is bound, specific adaptor proteins are recruited and bind to the death domain. Many of these adaptor proteins recruit initiator caspases to initiate apoptotic pathways. For example, initiator caspases 8 and 10 cleave mitochondrial proteins like BID which causes the release of cytochrome C and promotes the activity of effector caspases such as caspases 3 and 9. Once activated, effector caspases can directly degrade important cellular components such as actin, leading to apoptosis. In addition to these cytotoxic pathways, binding of the adaptor proteins to a death domain can also initiate signaling through JNK and NF-κB pathways.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us