Neurodegeneration
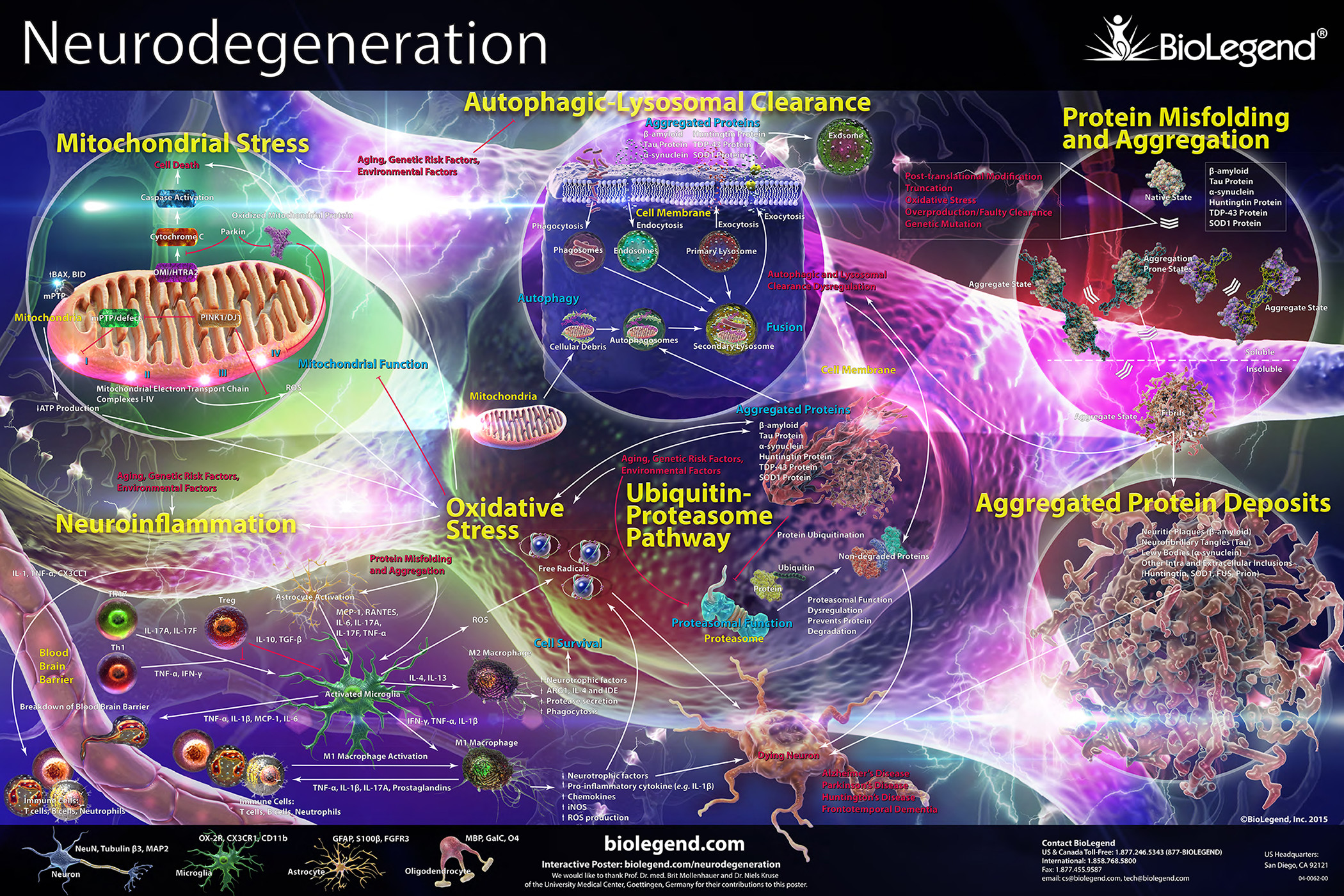
Neurodegeneration refers to the progressive deterioration and loss of the structure or function of neurons and is a hallmark of a variety of disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurodegeneration is a complex biological process that is often defined by the presence of misfolded protein aggregates that tend to form fibrils, inclusion bodies, and other large proteinaceous aggregates such as plaques. Protein misfolding and aggregation is influenced by a number of processes including genetic risk factors, mitochondrial and oxidative stress, ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy degradation pathways. In addition, many neurodegenerative disorders are associated with aberrant or disease related post-translational modifications of key target proteins that result in the disruption of normal protein folding leading to aggregation. Proteins prone to misfolding and aggregation include Amyloid-β and Tau in Alzheimer’s disease and α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
Then choose among our reagents, assays, and other tools to advance your research on neurodegenerative diseases. Learn more with our helpful Neurodegeneration Webpage.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us