Innate Immunity
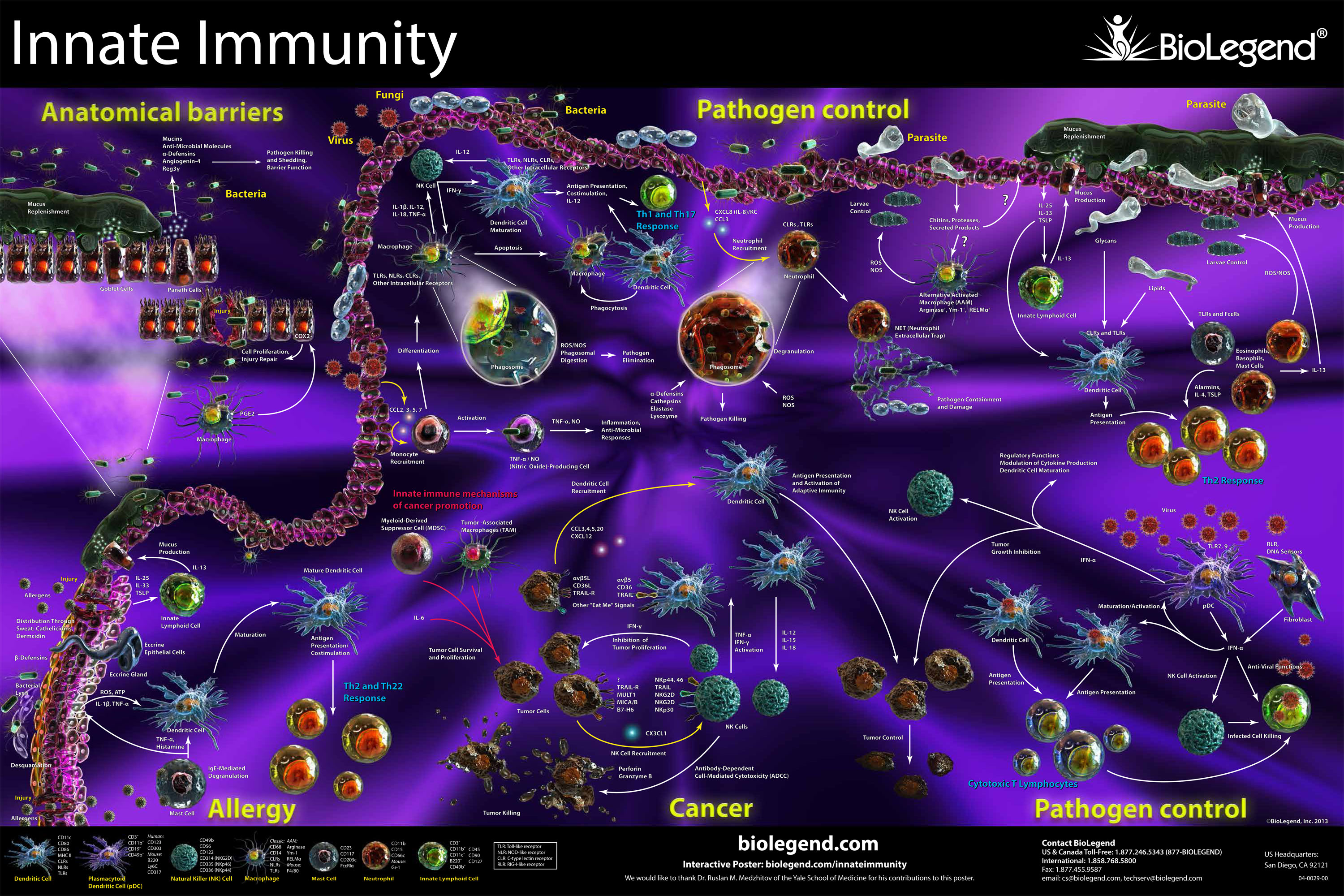
The innate immune system provides the initial line of defense against pathogens. The innate immune system includes anatomical barriers like epithelial barriers that product mucins and other anti-microbial peptides to kill pathogens. One major role of the innate system is to release cytokines and recruit other immune cells to the site of infection. Unlike the adaptive immune system, the innate immune system is non-specific and uses pattern-recognition receptors like TLRs to identify molecules common to pathogens. Antigen-presenting cells, like dendritic cells, interact with naïve T cells to drive their activation and differentiation into cytotoxic or helper cell subsets. Other cells in the innate immune system, like neutrophils, can directly engulf bacteria and produce additional cytokines to amplify immune signaling pathways. The innate immune system also plays a role in cancer and allergy.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us