Human Embryonic Stem Cell Pluripotency
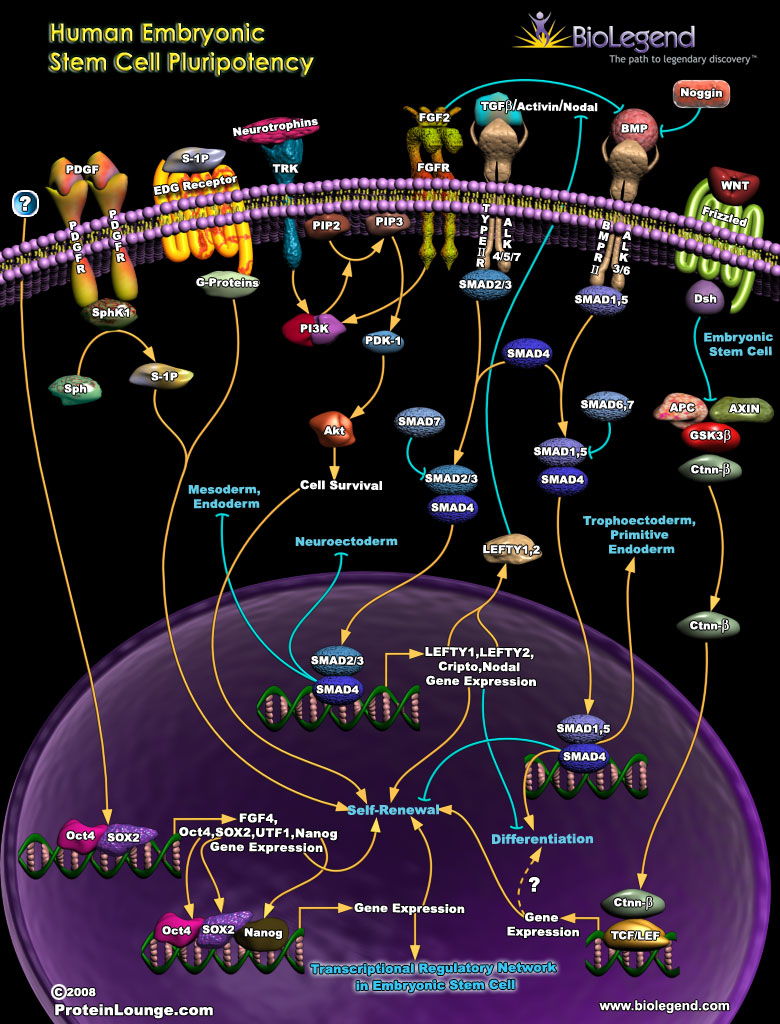
Human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) maintain their pluripotency through a variety of molecular signaling pathways. Extracellular proteins like PDGF, Neurotrophins, FGF, BMPs, and WNT regulate signaling cascades leading to stem cell renewal or differentiation. For example, signaling through BMPs activates SMAD signaling pathways. Once SMAD transcription factors translocate to the nucleus they regulate genes like LEFTY1, Cripto, and Nodal which promote self-renewal. Expression of other transcription factors like Oct4, Soc2, and Nanog also serve as part of the transcriptional regulatory networks that help to either maintain pluripotency or induce differentiation.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us