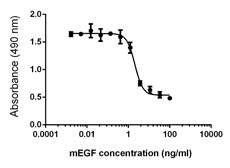
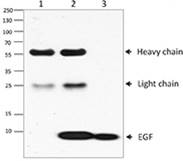
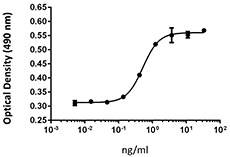
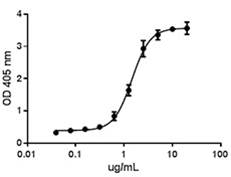
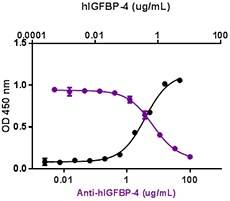
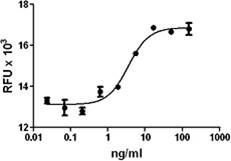
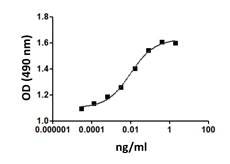
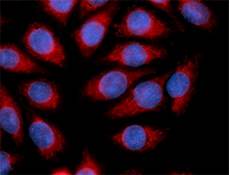
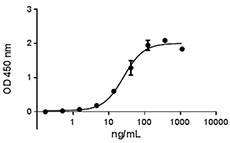
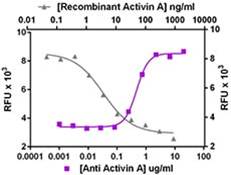
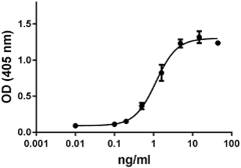
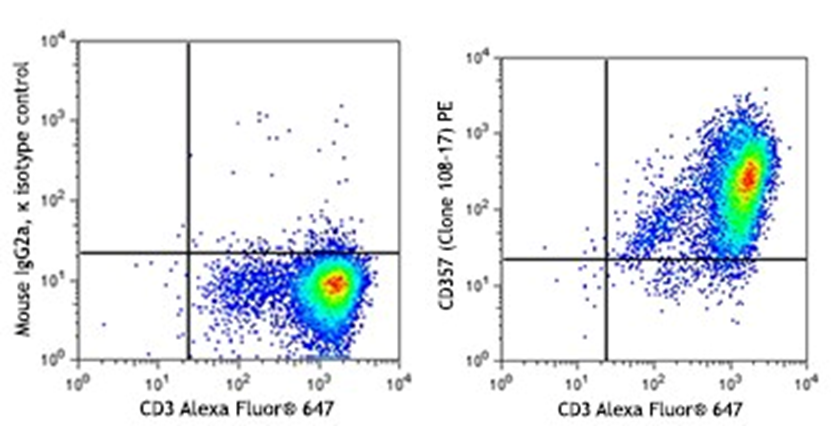
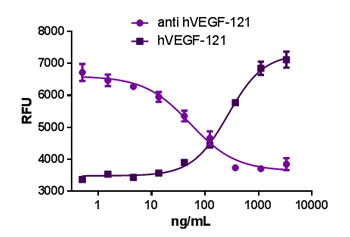
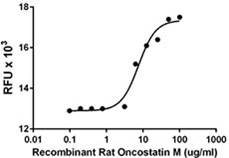
Growth factors are signaling molecules that regulate a number of critical cellular processes including proliferation, differentiation, migration, and development. Growth factors include both cytokines and hormones, which often initiate downstream signaling through binding to receptor tyrosine kinases on cellular surfaces. BioLegend offers a wide range of antibodies and recombinant proteins to study growth factors in a variety of applications including bioassays, ELISAs, multiplexing, Western blotting, flow cytometry and microscopy. View the sections below to learn more about the different growth factor families.
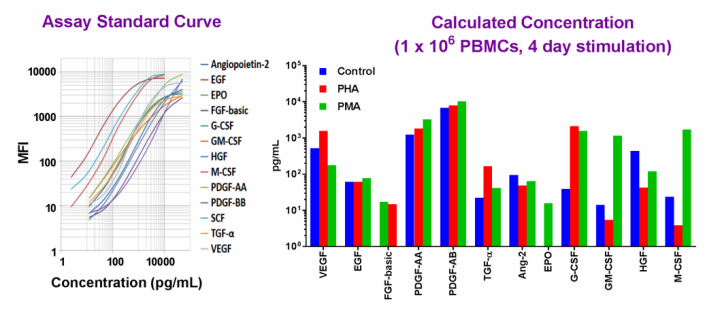
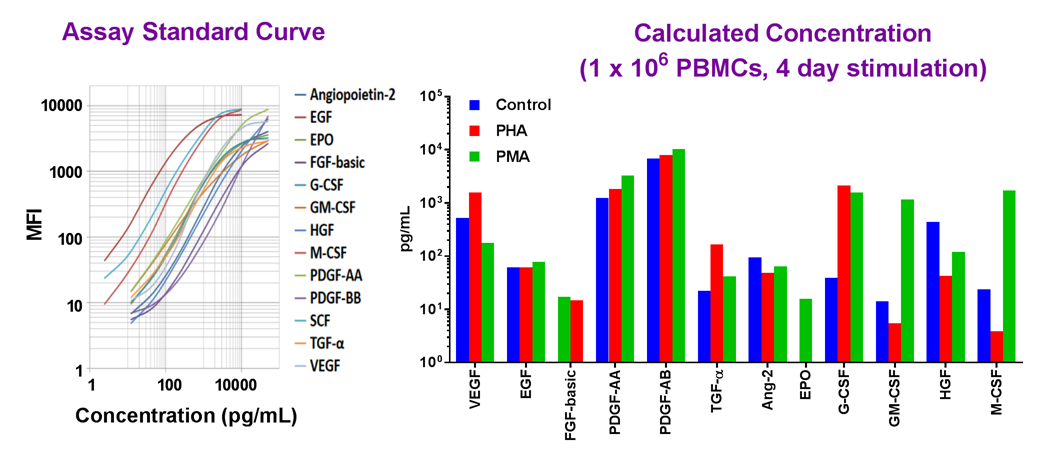
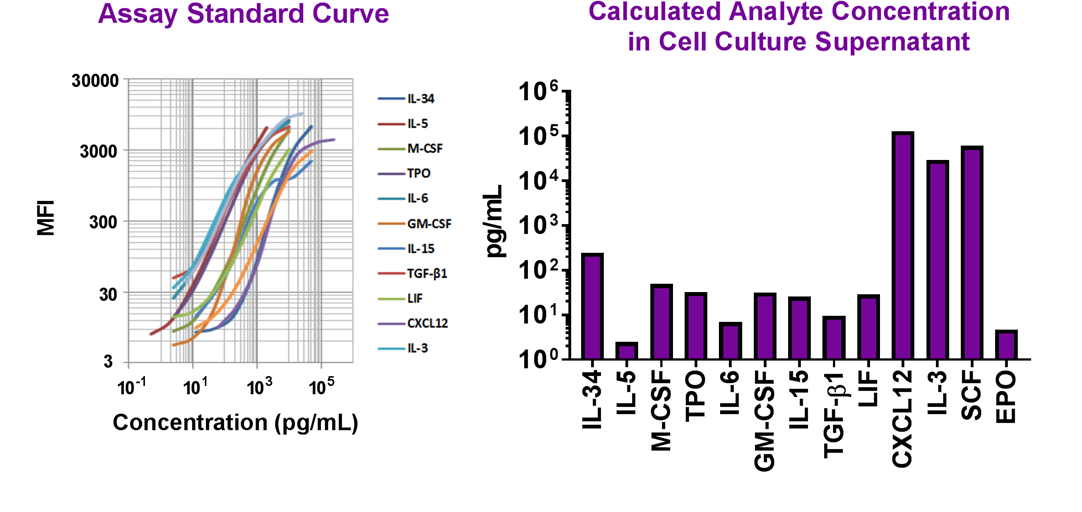
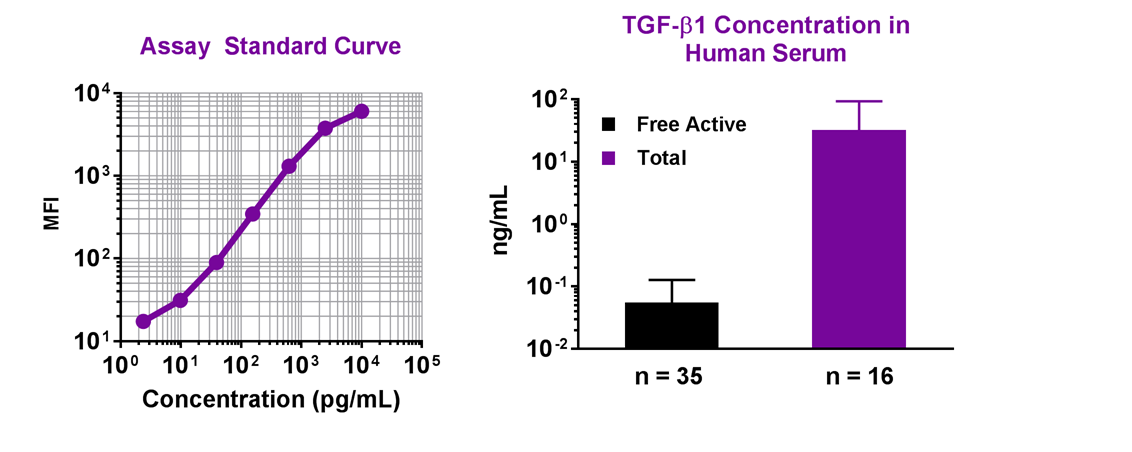
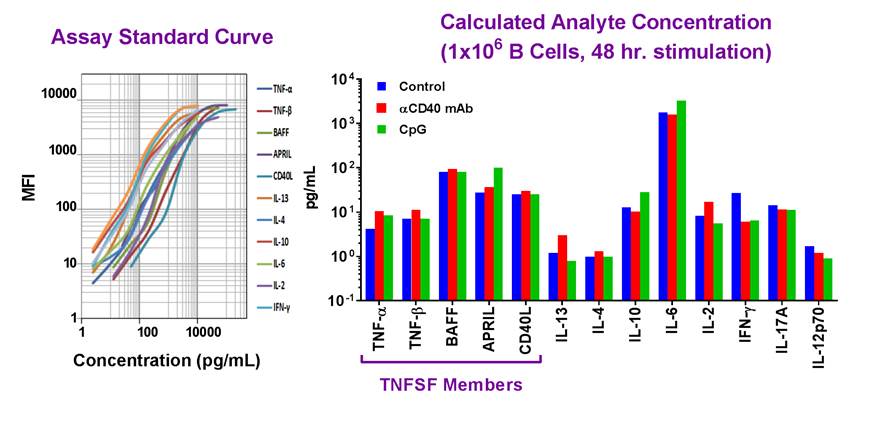
Simultaneously measure 13 human growth factors with our LEGENDplex™ bead-based immunoassay panel.
 Login/Register
Login/Register 






Follow Us