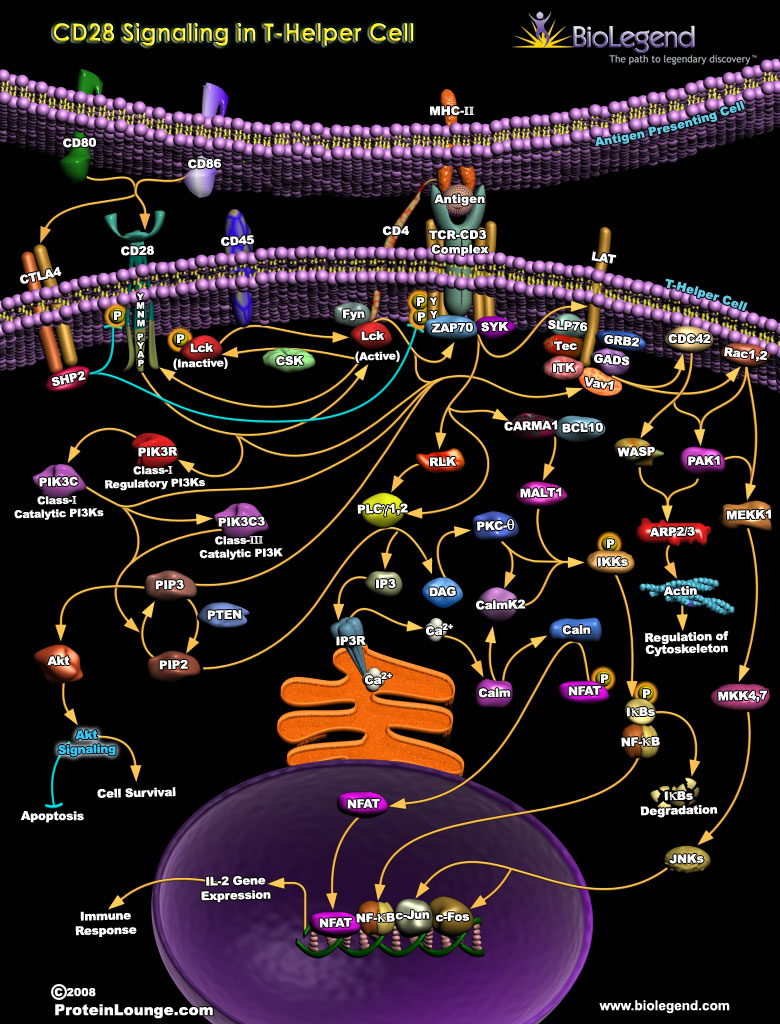
CD28 Signaling in T-Helper Cell
Antigen presenting cells (APCs) like dendritic cells and macrophages engage CD4+ helper T cell receptors (TCRs) with antigen-bound major histocompatiblity complex (MHC) II proteins. This is the first signal provided to the T cell. Signal 1 induces activation of Src kinases Lck and Fyn, which will phosphorylate the ITAMs of CD3. Lck also activates ZAP-70 which goes on to initiate signaling pathways that ultimately result in transcription factors (e.g. NFAT) activating gene expression. However, the first signal alone is not enough to activate CD4+ T cells. Without co-stimulation of CD28, TCR engagement often results in T cell anergy rather than activation. When fully stimulated by pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) like LPS, APCs also upregulate surface expression of co-stimulatory proteins CD80 and CD86. These ligands bind CD28 on the surface of CD4+ T cells, and give the T cell its second signal. If engaged by its ligands, CD28 is phosphorylated and recruits kinases to initiate signaling pathways. Kinases like JNK are activated and go on to promote expression of cytokines such as IL-2. Alternatively, if CD80/86 engages CTLA4 on the T cell, phosphorylation of the TCR complex and CD28 will be inhibited, and T cell activation will be prevented.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login/Register
Login/Register 







Follow Us