- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor® 647, Streptavidin-AF647
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
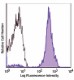
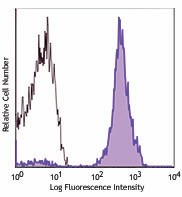
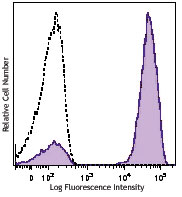
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with biotinylated CD3 (filled histogram) or biotinylated mouse IgG1 isotype control (open histogram), followed by SAV-Alexa Fluor® 647.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 405237 | 100 µg | $206 | ||||
Streptavidin binds to biotin with high affinity. Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor® 647 is useful for detecting biotinylated antibodies. The excitation of Alexa Fluor® 647 by 633 nm / 635 nm laser light induces a light emission maximum of 668 nm.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, All Species
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- Streptavidin was conjugated with Alexa Fluor® 647 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml (concentration relates to the Streptavidin only component of the conjugate)
- Storage & Handling
- The streptavidin-Alexa Fluor® 647 solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
ICFC - Verified
- Recommended Usage
-
This streptavidin product is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. The concentration provided is based upon molecular mass of streptavidin independent of any additional molecular mass that might be added by the Alexa Fluor® 647 conjugation. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.125 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* Alexa Fluor® 647 has a maximum emission of 668 nm when it is excited at 633 nm / 635 nm.
Alexa Fluor® and Pacific Blue™ are trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation.
View full statement regarding label licenses - Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor® 647 is useful as a second step reagent for indirect immunofluorescent staining, when used in conjunction with biotinylated primary antibodies. The average molecular weight of Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor® 647 is 60 kD and Streptavidin alone is 52 kD.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Chappaz S, et al. 2007. Blood doi:10.1182/blood-2007-02-074245.
- Nishimoto KP,et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 181:4010.PubMed
- Niki T, et al. 2009. J. Biol. Chem. 284:32344. PubMed
- Shibui A, et al. 2011. Exp Parasitol. 129:318. PubMed
- Scatizzi JC, et al. 2012. J. Immunol. 188:3307. PubMed
- Yamakawa N, et al. 2012. Int Immunol. PubMed
- Shibata T, et al. 2012. Int Immunol. 24:613. PubMed
- Baccala R, et al. 2012. J. Immunol. 189:5976. PubMed
- Grevers LC, et al. 2013. Ann Reheum Dis. 72:278. PubMed
- Woo SJ, et al. 2013. J Leukoc Biol. 93:363. PubMed
- Ashbaugh JJ, et al. 2013. J. Immunol. 190:4525. PubMed
- Reading JL, 2013. J. immunol. 190:4542. Pubmed.
- Kanno A, et al. 2013. Int Immunol. 25:413. PubMed
- Gunaydin G, et al. 2014. Vaccine. 32:470. PubMed
- Shade KT, et al. 2015. J Exp Med. 212:457. PubMed
- Product Citations
-
Antigen Details
- Gene ID
- NA
- UniProt
- View information about Biotin on UniProt.org
 Login/Register
Login/Register 












Follow Us