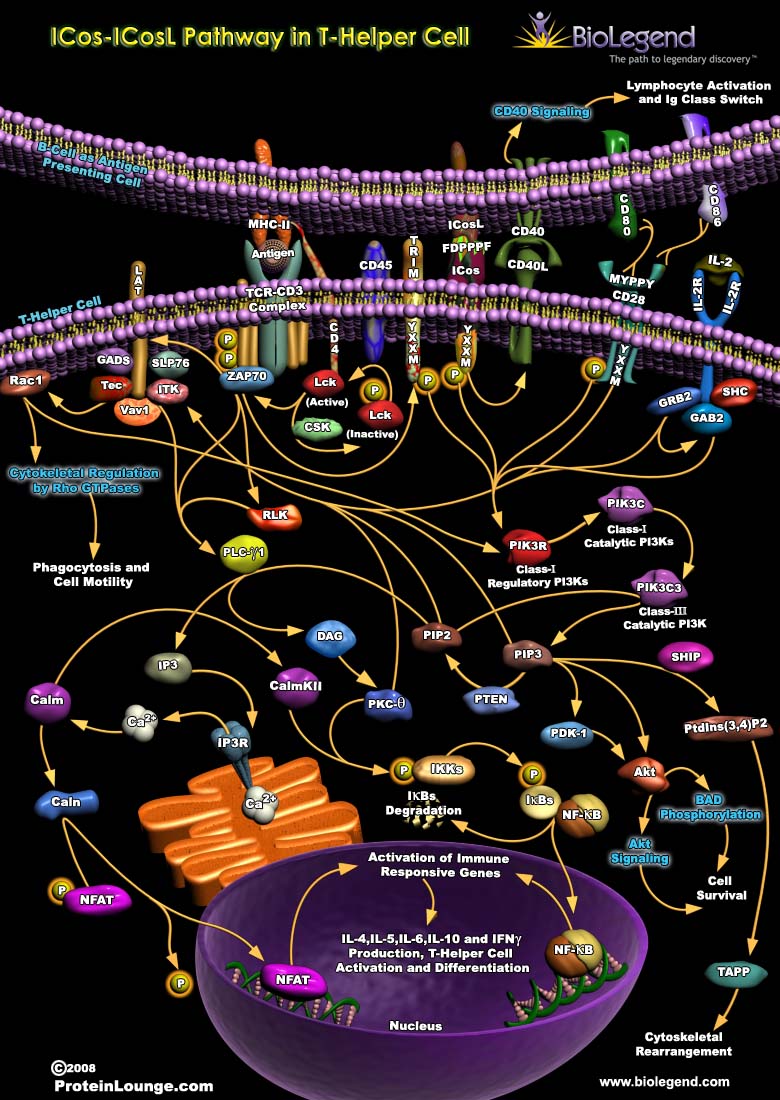
ICos-ICosL Pathway in T-Helper Cell
ICos, also known as CD278, is a costimulatory molecule expressed on T helper cells, particularly Th1 and Th2 cells. T cells require two different signals to become fully activated. One signal is antigen-specific and occurs through binding of MHC on an antigen-presenting cell (APC) with the TCR, and the other is a co-stimulatory signal which is not antigen-specific. One example of a co-stimulatory signal is the binding of ICosL on the surface of the APC to ICos on the T helper cell. Once bound, phosphorylation of ICos initiates signaling cascades through a number of intermediates including NFκB signaling pathways. Once activated by IKKs, NF-κB translocates to the nucleus where it can activate immune responsive genes to induce cytokine production or regulate T helper cell activation and differentiation.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login/Register
Login/Register 







Follow Us