EGF Pathway
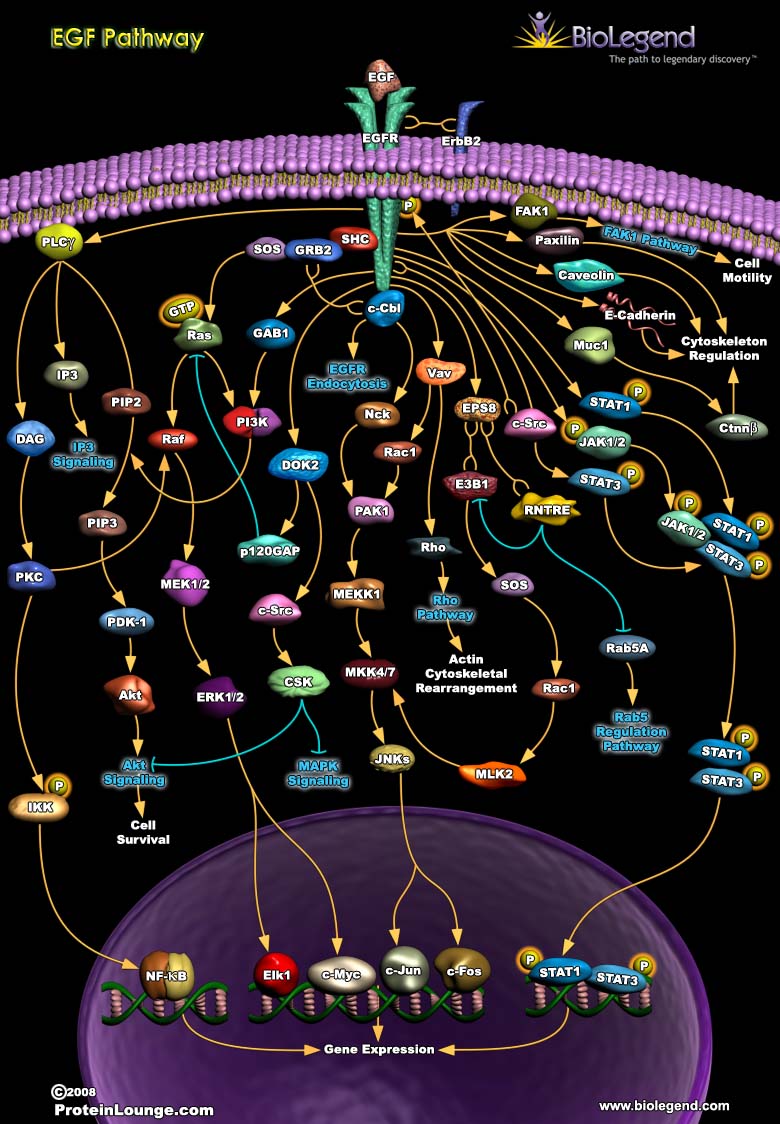
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, also known as ErbB1) binds to a number of endogenous ligands, including EGF, epiregulin, and transforming growth factor α (TGFα), that regulate cell growth and proliferation. Upon binding of ligand, EGFR forms homodimers or heterodimers with ErbB2, and initiates signals through its cytoplasmic kinase domain. This leads to recruitment of signaling proteins like SH2, GRB2, and SOS, which results in the activation and nuclear translocation of ERK. GAB proteins are also recruited, which activate PI3K for conversion of PIP2 to PIP3, leading to AKT signaling for cell survival. EGFR binding can trigger PLCγ activity, which leads to IP3 and DAG generation and the transduction of the PKC pathway and NF-κB activation. Other pathways induced by EGFR include JAK-STAT, JNK, and FAK1 signaling.
Click on the poster below to view the interactive version.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 







Follow Us